How to Delete Focus Builder
Published by: NeurdSolutions LLCRelease Date: April 30, 2024
Need to cancel your Focus Builder subscription or delete the app? This guide provides step-by-step instructions for iPhones, Android devices, PCs (Windows/Mac), and PayPal. Remember to cancel at least 24 hours before your trial ends to avoid charges.
Guide to Cancel and Delete Focus Builder
Table of Contents:

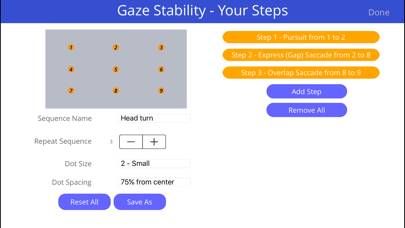
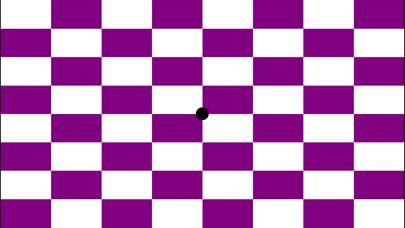
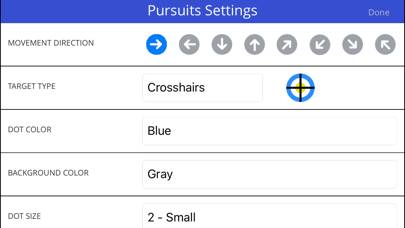
Focus Builder Unsubscribe Instructions
Unsubscribing from Focus Builder is easy. Follow these steps based on your device:
Canceling Focus Builder Subscription on iPhone or iPad:
- Open the Settings app.
- Tap your name at the top to access your Apple ID.
- Tap Subscriptions.
- Here, you'll see all your active subscriptions. Find Focus Builder and tap on it.
- Press Cancel Subscription.
Canceling Focus Builder Subscription on Android:
- Open the Google Play Store.
- Ensure you’re signed in to the correct Google Account.
- Tap the Menu icon, then Subscriptions.
- Select Focus Builder and tap Cancel Subscription.
Canceling Focus Builder Subscription on Paypal:
- Log into your PayPal account.
- Click the Settings icon.
- Navigate to Payments, then Manage Automatic Payments.
- Find Focus Builder and click Cancel.
Congratulations! Your Focus Builder subscription is canceled, but you can still use the service until the end of the billing cycle.
How to Delete Focus Builder - NeurdSolutions LLC from Your iOS or Android
Delete Focus Builder from iPhone or iPad:
To delete Focus Builder from your iOS device, follow these steps:
- Locate the Focus Builder app on your home screen.
- Long press the app until options appear.
- Select Remove App and confirm.
Delete Focus Builder from Android:
- Find Focus Builder in your app drawer or home screen.
- Long press the app and drag it to Uninstall.
- Confirm to uninstall.
Note: Deleting the app does not stop payments.
How to Get a Refund
If you think you’ve been wrongfully billed or want a refund for Focus Builder, here’s what to do:
- Apple Support (for App Store purchases)
- Google Play Support (for Android purchases)
If you need help unsubscribing or further assistance, visit the Focus Builder forum. Our community is ready to help!
What is Focus Builder?
Focus builder eye training:
Eye movements are a very powerful way to exercise the brain and to create long-term change in the brain, known as plasticity. The “Focus Builder” app contains a variety of exercises which challenge users to voluntarily move their eyes in various patterns, speeds and directions, which have been proven to activate specific parts of the brain depending on which eye movement is performed.
This app is specifically designed for doctors that specialize in Functional Neurology and their patients. There is currently no app available that can provide these specific exercises. For best results, patients should consult a Functional Neurologist to determine how to use this app according to their needs and obtain the most therapeutic value.
There are 3 types of eye movements that can have profound therapeutic benefits and all three are available in this app.
1.Pursuits (slow eye movements): Smooth pursuit eye movements allow the eyes to closely follow a moving object. Most people are unable to initiate pursuit without a moving visual signal. The pursuit of targets moving with velocities of greater than 30°/s tend to require catch-up saccades.
2.Saccades (fast eye movements): Saccades are quick, simultaneous movements of both eyes in the same direction. Initiated cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for fixation, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic nystagmus.
3.Anti-saccades (look away): The anti-saccade task has emerged as an important task for investigating the flexible control that we have over behavior. In this task, participants must suppress the reflexive urge to look at a visual target that appears suddenly in the peripheral visual field and must instead look away from the target in the opposite direction. A crucial step involved in performing this task is the top-down inhibition of a reflexive, automatic saccade. Patients diagnosed with various neurological and/or psychiatric disorders that affect the frontal lobes or basal ganglia find it difficult to suppress the automatic pro-saccade, revealing a deficit in top-down inhibition.